Understanding Incoterms
Introduction to Incoterms
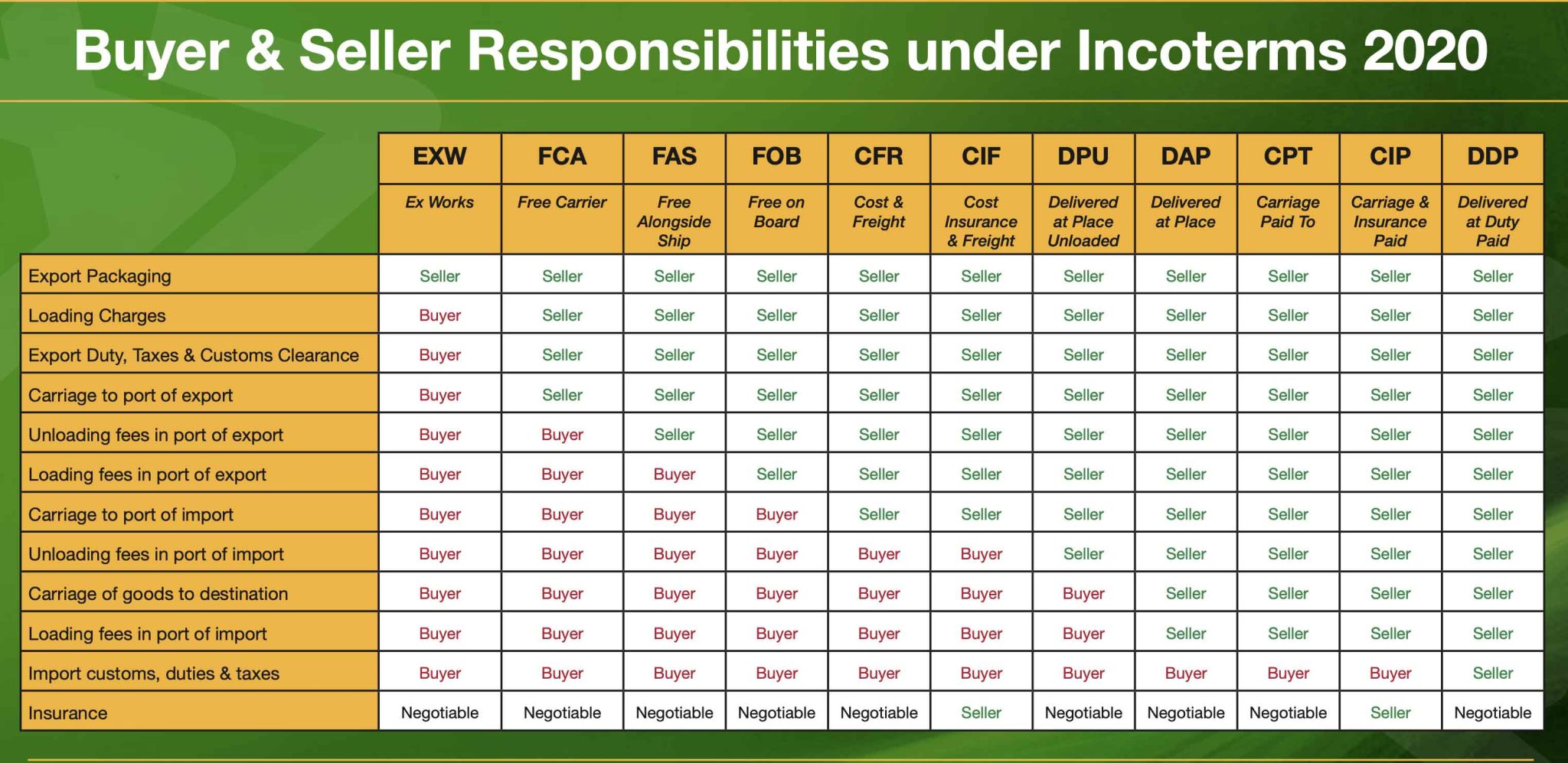
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a globally recognized set of rules defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the transportation of goods. They determine who is responsible for costs, risks, and liabilities at different stages of the shipping process.
Designed to simplify international trade, Incoterms like FOB, CIF, and EXW help ensure that both parties understand their roles, enabling smoother transactions. This guide aims to provide insights into commonly used Incoterms and their implications for buyers and sellers.
Key Concepts
The main purpose of Incoterms is to outline which party handles specific responsibilities, such as export customs clearance, insurance, and delivery costs. For instance, EXW places most responsibilities on the buyer, while DDP ensures the seller takes on all delivery-related duties.
Understanding these terms allows businesses to negotiate effectively and minimize misunderstandings during transactions.
Commonly Used Incoterms
EXW (Ex Works): The buyer is responsible for all arrangements and costs starting from the seller's premises.
FOB (Free On Board): The seller covers costs up to the loading of goods onto the ship; the buyer takes responsibility from there.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The seller covers shipping and insurance up to the port of discharge, but risks transfer to the buyer once goods are loaded.
DAP (Delivered at Place): The seller delivers the goods to the agreed location, with the buyer responsible for unloading and import duties.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The seller handles all shipping responsibilities, including duties and taxes, providing a hassle-free experience for the buyer.
Advanced Topics
Selecting the right Incoterm is critical for managing risks and costs effectively. For example, choosing FOB offers buyers greater control over shipping processes, while CIF is advantageous for sellers looking to ensure goods are insured during transit.
In complex transactions involving multiple modes of transport, terms like CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid) provide flexibility and additional coverage for goods during transit.
By fully understanding Incoterms, businesses can navigate international trade with confidence, ensuring compliance with global standards and avoiding costly misunderstandings.
"Trade without clarity leads to disputes; Incoterms bring that clarity."